Summary
- Pattern making is a crucial step in collection creation
- The process can be done manually or digitally, offering various advantages
- Manage your production effectively with Audaces360 multi-solution! Sign up now for a free trial.
Clothing pattern making stands as a pivotal process in the realm of fashion collection creation.
This stage marks the transition from conceptual ideas to tangible garments. To achieve the desired results, it’s imperative to choose the right patternmaking method for your fashion company.
In this article, we’ll delve into the significance of patternmaking in ensuring your pieces match your vision.
Additionally, we’ll explore both flat pattern making and draped patterns.
Sumário
Let’s embark on this enlightening reading!
What is pattern making?
Clothing pattern making is a fundamental process in the development of a fashion collection. It entails the creation of simplified representations of garments, resulting in patterns or templates for those garments.
This process holds immense importance in both the design and production phases, as it enables the precise production of garments in various sizes and tailored to different body types.
Through pattern making, the primary goal is to gain a comprehensive understanding of how a garment should fit, anticipate its outcome, and conduct simulations to test various hypotheses.
Achieving excellence in clothing patternmaking requires a skill set and technical knowledge encompassing areas such as geometry, mathematics, statistics, and technical drawing.
Learn more: 6 pattern making courses to enhance your skills
How is the pattern making process?
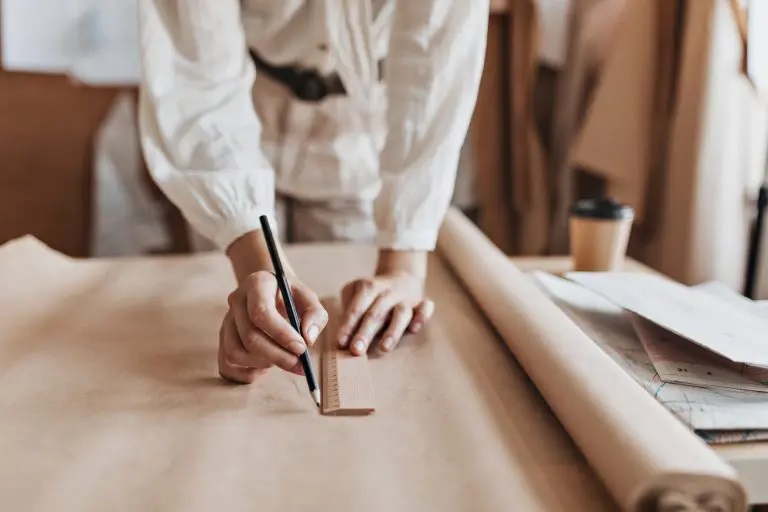

The pattern making process can vary depending on the designer, the type of garment being created, or the ultimate goal of the process.
However, in general, modeling a piece of clothing involves a set of similar steps.
Below, you can explore the 10 key stages of the patter making procedure:
Design
The fashion stylist begins by sketching the desired garment design. This creative process may involve hand-drawn sketches or the use of fashion design software like Audaces Fashion Studio.
Fabric selection
Careful consideration goes into selecting the fabric for the garment’s production. The choice of fabric can significantly impact the fit and final appearance of the clothing. Hence, it’s vital to explore all available options before making a selection for your project.
Measurement taking
Precise measurements are taken and meticulously recorded. These measurements encompass various aspects, including shoulder width, bust, waist, hips, arm and leg lengths, and more.
Pattern block creation
Using the recorded measurements, the initial pattern is crafted (also called pattern block or “sloper”). This pattern can be made on paper, fabric, or digitally, serving as a representation of the body’s size and shape.
Pattern adjustment
The pattern undergoes adjustments according to the stylist’s preferences, which may involve alterations in length, width, curves, and overall shapes.
Fabric cutting
Precisely following the adjusted pattern, the fabric is cut. Accuracy in fabric cutting is crucial to ensure a well-fitting garment.
Sewing
The fabric pieces are meticulously sewn in accordance with the stylist’s pattern. The sewing process often involves multiple steps, including fittings and final adjustments.
Finishing
Following the sewing phase, attention is directed to the finishing details. This involves tasks such as trimming loose threads, attaching buttons and zippers, adding linings, and incorporating any other desired stylistic elements.
Fitting trials
A model wears the garment for fit testing and adjustments. This step ensures that the clothing fits perfectly and meets the stylist’s specifications.
Garment production
Once the garment passes the fit test and receives approval, the pattern serves as the blueprint for producing the piece in various sizes and quantities.
What is the significance of pattern making?
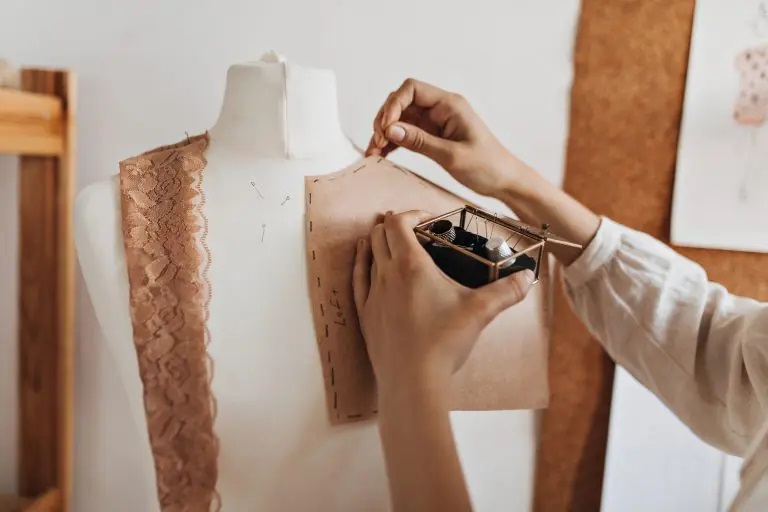

As you embark on the project of planning a clothing collection, the initial sketches and concepts serve as your foundation. However, it’s in the meticulous process of crafting each piece that the true advantages become evident.
Clothing pattern making holds immense importance for both the fashion industry and its discerning customers.
This significance stems from its ability to ensure the creation of garments characterized by enhanced comfort, personalized fit, superior quality, and innovative design.
Below, we’ll see some reasons why this activity makes all the difference:
Fit and comfort
Pattern making accommodates various body sizes and shapes, ensuring garments offer a comfortable and well-fitting experience for customers.
Time and resource savings
The process allows for the rapid and efficient mass production of garments, resulting in significant time and resource savings.
Creativity
Designers have the freedom to craft distinctive and innovative pieces, exploring novel shapes, textures, and fabrics to push the boundaries of fashion.
Quality assurance
Clothing pattern making is fundamental to the quality of garments, guaranteeing a superior fit, impeccable finish, and increased durability.
Standardization
Consistent patterns are generated, ensuring that consumers can find clothing in the same size across different stores, promoting ease and convenience in shopping.
Learn more: Discover the benefits of digital sewing patterns and how they work
Which are the main pattern making techniques?
The primary techniques for clothing pattern making encompass two distinct approaches: flat pattern making and three-dimensional draping (also known as “moulage”, in French).
To gain a deeper understanding of these methods and their respective uses, check out the details below:
Flat pattern making
Flat pattern making is a technique for creating garment patterns using flat fabrics and paper templates, often referred to as 2D modeling.
The process commences with a fashion sketch or design concept.
Subsequently, the stylist utilizes precise measurements and calculations to draft a two-dimensional pattern on paper.
The chief advantage of flat pattern making lies in its precision, allowing stylists to visualize the garment in its actual size and make necessary adjustments based on body measurements and client preferences.
Moreover, flat modeling proves exceptionally valuable for efficient mass production, as it involves repetitive steps, facilitating the creation of numerous identical pieces within a short timeframe.
However, it is not without its drawbacks. Flat pattern making is comparatively less flexible when compared to three-dimensional (3D) modeling techniques.
Additionally, it may present a steeper learning curve for novice stylists.
The decision to adopt the flat patterning technique should hinge on the specific requirements of your garment project.
If your objective involves large-scale production, flat pattern making may be an ideal choice.
Learn more: How to incorporate digital patterns into your production
Three-dimensional pattern (draping or moulage)
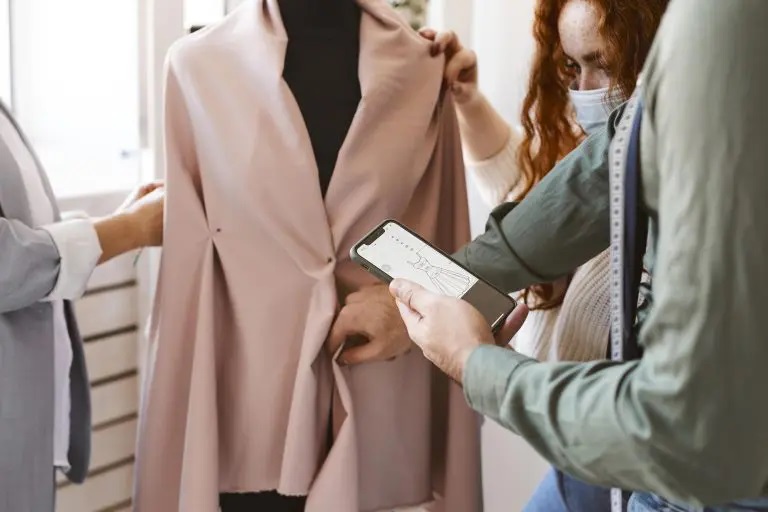

The term “Moulage” originates from French, signifying “form”. This method, which dates back to the 1920s, was pioneered by two French stylists, Madeleine Vionnet and Alix Grés.
In contrast to flat pattern making, the draping method, also known as moulage, involves the direct creation of a garment on a mannequin or a live model.
This approach allows for a visualization of the garment’s fit even before its completion. Renowned for its artistic flair, three-dimensional modeling has found favor, especially in haute couture.
In the realm of three-dimensional modeling, the fabric is skillfully folded, pleated, and pinned around the mannequin, resulting in a three-dimensional pattern for the garment.
Subsequently, these patterns are cut and sewn to produce the final piece.
This technique offers the unique advantage of working directly with the fabric, permitting adjustments to the garment during the modeling process.
Moulage excels in its ability to provide an immediate 3D visualization of the piece at the outset of the manufacturing process.
Furthermore, it empowers designers to craft shapes and volumes that might prove challenging with other modeling methods.
However, it’s essential to acknowledge that moulage does have its drawbacks.
It typically consumes more time compared to alternative modeling techniques, potentially driving up production costs.
Successfully executing this method demands skill, practice, and a certain level of expertise.
Learn more: 10 tips to master the moulage technique and improve your garment modeling
What’s the difference between industrial and bespoke pattern making?
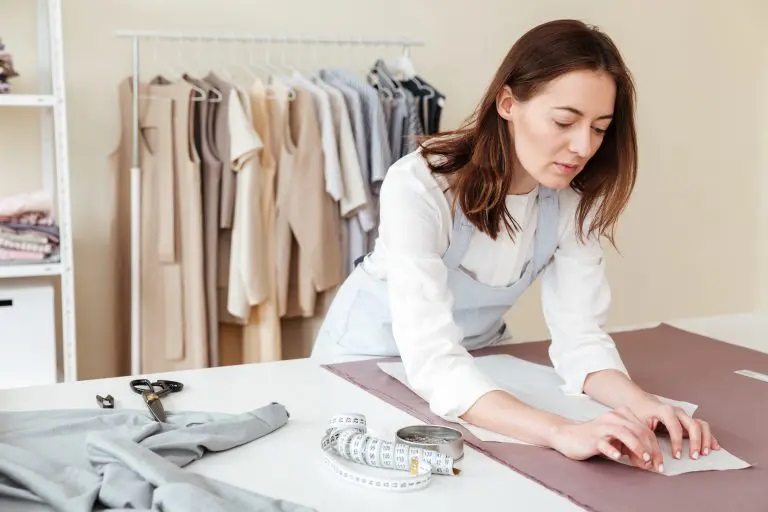

Industrial and bespoke pattern making are distinct approaches to the art of creating garments.
Industrial pattern making is primarily geared towards mass production, where patterns are generated and replicated in large quantities.
This method relies on standardized measurements from sizing charts or parameters, resulting in garments designed to fit various sizes without the need for individual adaptations.
Conversely, bespoke pattern making is tailored to each individual, meticulously adjusted to their unique body measurements.
This technique is founded on the specific dimensions of the customer, enabling the creation of a one-of-a-kind piece that perfectly conforms to their silhouette.
Bespoke pattern making finds its most prominent application in haute couture, where the pursuit of exclusivity and an impeccable fit takes precedence.
Another notable disparity between these two methods lies in both the time required for production and the associated costs.
Industrial pattern making is characterized by its speed and cost-effectiveness, benefiting from the economies of scale inherent in large-scale production and the use of standardized measures.
In contrast, tailor-made patterns demand more time and incur higher expenses due to the creation of individualized pieces, each meticulously crafted to suit the unique body type of every client.
Learn more: Discover the benefits of a pattern grading chart for your clothing production
How to get started with clothing pattern making?
When it comes to pattern making, there are two primary methods: manual and digital.
Each one possesses distinct characteristics that influence the selection by clothing companies in their operations.
Explore both techniques to determine which aligns best with your company’s objectives.
Traditional paper pattern making
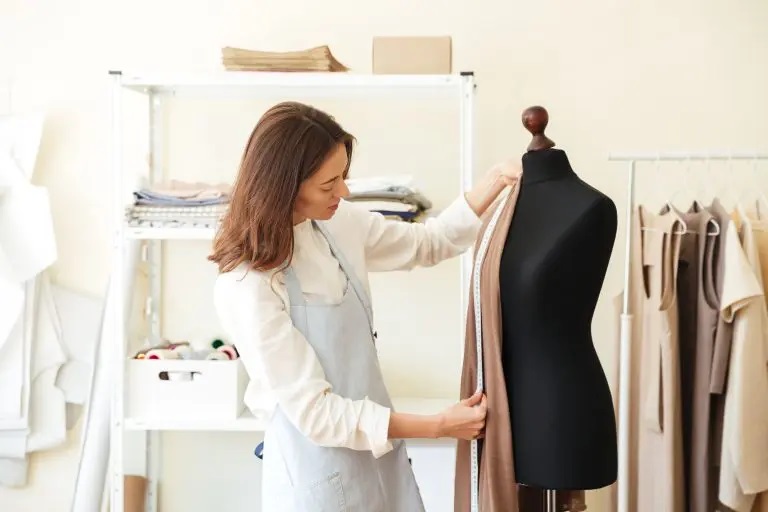

While this method has a long history, it remains a prevalent choice in large-scale production.
It starts with the creation of a sample garment, carefully tailored to ensure an approved fit, defined characteristics, and any necessary adjustments.
Once the sample is perfected, it serves as the foundation for producing additional pieces.
After this initial stage, the sample is carefully disassembled and meticulously laid out. This process optimizes fabric usage and minimizes waste.
Moreover, traditional paper pattern making is also instrumental in the creation of graded patterns, a practice that involves adjusting the sizing of patterns to accommodate various body measurements.
Digital pattern making
Digital pattern making leverages technology and software to create garment patterns.
This innovative process provides the capability to visualize and simulate clothing designs in both 2D and 3D environments.
The advantages of digital clothing pattern making are significant. It offers enhanced precision during pattern creation, reducing errors and the need for rework.
Furthermore, digital modeling conserves resources and streamlines the prototyping timeline.
Digital patterns are highly flexible, allowing for easy modifications and updates without incurring additional costs.
Additionally, this form of modeling facilitates seamless cross-industry communication, as patterns can be easily shared online among stakeholders.
Learn more: What digital sketching is and how to apply it to your fashion collection
Discover how Audaces can enhance pattern makers efficiency
Let’s delve into the various Audaces solutions designed to streamline pattern-making workflows and boost efficiency.
Audaces360
Audaces introduces Audaces360, a cutting-edge solution that seamlessly bridges the creative and production phases, significantly enhancing efficiency and profitability in the fashion industry.
One of its standout features is its holistic view and real-time control of the production process, facilitated by complementary tools that provide accurate information at every stage.
This real-time data empowers faster and more effective decision-making.
Audaces360’s multifaceted capabilities inject agility into the production of garments, enabling customers to personalize their orders, thereby diversifying the product range.
Reduced inventory leads to cost savings, ultimately bolstering profits!
Audaces Pattern
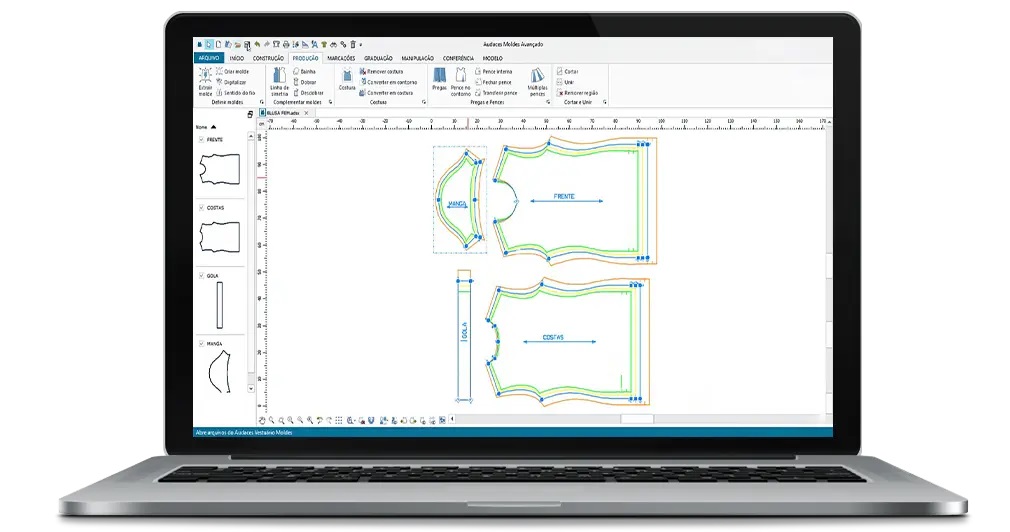
Audaces Pattern stands as a formidable technological solution, offering invaluable support to those in pursuit of heightened efficiency and agility in collection production.
Its user-friendly and intuitive interface facilitates the creation of digital patterns at a staggering 70% faster rate compared to manual methods.
A standout feature of Audaces Pattern is its automatic measurement table, a game-changer in the development of intricate patterns and the streamlining of grading processes, rendering the use of paper obsolete.
This swift and profit-driven technology optimizes production timelines, resulting in substantial cost reductions.
Audaces Marker
Efficient resource management is paramount to the profitability of any fashion enterprise.
Audaces Marker offers a solution to enhance resource management, ensuring maximum fabric utilization and optimizing manual markings by up to 13%.
Audaces’ automated fitting system facilitates rapid fitting of any garment piece, expediting the production process and enhancing delivery timelines.
Moreover, customization options allow for tailored production, accommodating the unique requirements of each garment.
With Audaces Marker, increased efficiency and cost reduction become achievable goals, making significant contributions to the success of your business.
Audaces Digiflash
Audaces Digiflash is specialized software designed to streamline the digitization of clothing patterns.
It empowers pattern makers to convert traditional paper patterns into digital files compatible with cutting machines and printers.
This versatile tool enables the precise and rapid capture of images from physical patterns, transforming them into editable digital files.
This functionality simplifies the process of adjusting measurements and crafting new patterns with ease.
Audaces Digiflash serves as a powerful solution, introducing heightened agility and efficiency into the pattern-making process.
Beyond efficiency, it contributes to cost reduction and elevates the overall quality of the garments produced.
Discover how Audaces Digiflash bridges the gap between traditional and digital pattern making, revolutionizing your production workflow.
Conclusion
If you aspire to streamline your pattern-making process efficiently and rapidly while maintaining a high standard of quality, it’s essential to explore software solutions that can elevate your day-to-day production.
These tools not only offer precision but also contribute to material conservation, ultimately enhancing the accuracy of your collection development.
Eager to deepen your understanding of this topic?
Then download our free e-book and gain insights into how digital modeling operates within the Audaces system:
FAQ
Pattern making is a crucial step in fashion collection development, involving the creation of simplified garment representations or templates.
The clothing pattern making process varies based on factors like the designer, garment type, and objectives. Generally, it involves similar steps for modeling clothing pieces.
Pattern making is vital for both the fashion industry and customers, ensuring comfortable, customized, high-quality, and innovative garments.










