Summary
- Learn what Industry 5.0 means and how it differs from previous industrial revolutions.
- Explore how the human touch and advanced technology come together in the apparel business.
- Ready to optimize your fashion company? Subscribe to our newsletter to receive more tips!
Over the years, technology has transformed everything in fashion, from design to production and sales. Now, a new era is emerging. One that redefines the relationship between humans and machines. This is the era of Industry 5.0.
Unlike Industry 4.0, which focused mainly on automation and digitalization, Industry 5.0 puts the human element in the center. It promotes collaboration between people and intelligent systems, emphasizing creativity, ethics, and sustainability.
So, if you don’t want to get left behind, it’s time to grasp everything about the subject. After all, the future of fashion is human-centered, creative, and ethical – and it’s already here.
Happy reading!
Sumário
What is Industry 5.0?
Industry 5.0 represents the next evolution in industrial development. One that brings the human element back into the center of innovation.
Unlike previous revolutions that focused primarily on automation, Industry 5.0 promotes collaboration between humans and intelligent machines. It’s about creating synergy between technology and creativity to achieve smarter, more sustainable, and more personalized production.
This new era focuses on balance. Instead of replacing workers, it empowers them with digital tools such as Artificial Intelligence, robotics, and data analysis.
The goal is to allow people to make better decisions, improve efficiency, and add emotion and creativity. These are values that machines alone cannot provide.
Differences between Industry 5.0 and previous generations
To understand what makes Industry 5.0 so transformative, it’s important to look back. Each industrial era before introduced new technologies that reshaped production and society.
Industry 1.0
The First Industrial Revolution began in the late 18th century. It marked the transition from manual labor to mechanized production.
It was the introduction of the steam engine that revolutionized manufacturing, enabling faster and more consistent output. Factories replaced small workshops, and industries such as textiles became the first to experience mass production.
Industry 2.0
The Second Industrial Revolution emerged between the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Electricity became widespread, and innovations like the assembly line transformed production systems. Efficiency and standardization became the new goals of industrial development.
For textiles, this period meant even faster manufacturing. Sewing machines and electric looms increased productivity, and the introduction of ready-to-wear clothing began shaping consumer behavior.
Industry 3.0
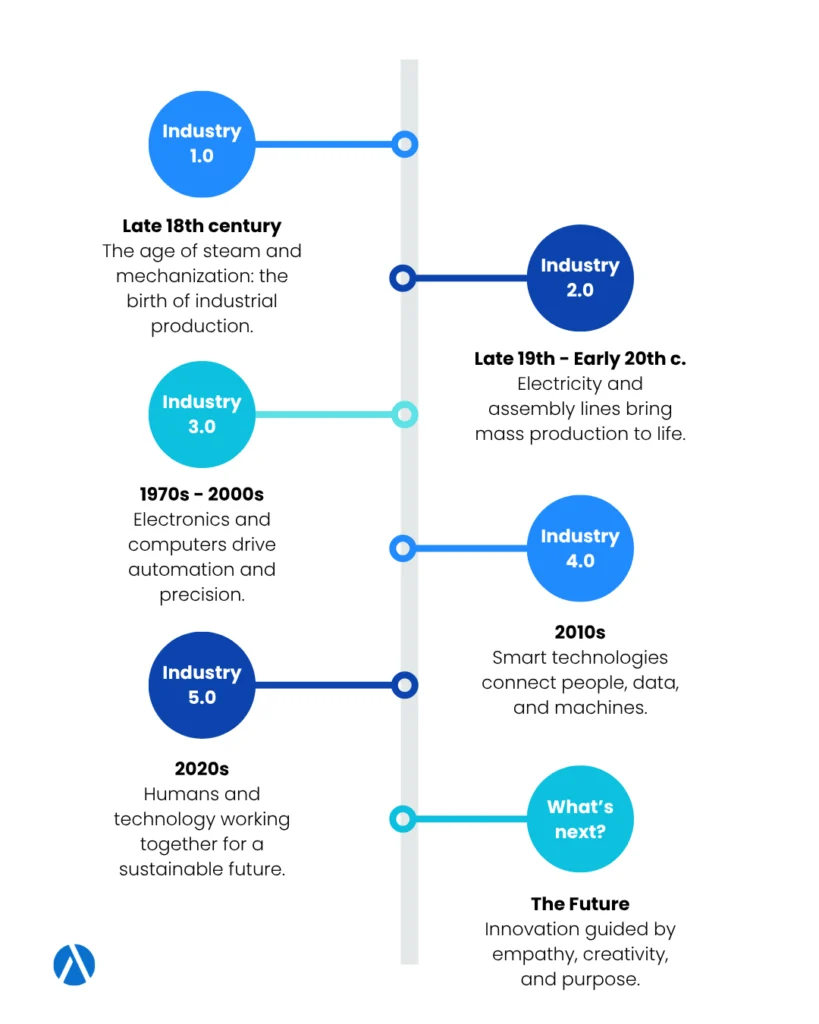
The Third Industrial Revolution, starting in the 1970s, marks the introduction of electronics, computing, and automation.
Machines became smarter and production lines started to include programmable systems. Information technology became essential for managing operations and logistics.
This digital evolution made global production networks possible. Brands could design in one country and manufacture in another, leading to the globalization of the fashion supply chain. However, with these advances came new challenges, including ethical concerns around labor and overproduction.
Industry 4.0
The Industry 4.0 emerged in the 21st century. It integrated advanced digital technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data analytics.
This stage connected machines, systems, and people in real time, enabling smart manufacturing and more data-driven decisions.
For fashion companies, the fourth industrial revolution represented a shift toward digital transformation. Virtual prototyping, 3D modeling, and automated cutting systems allowed faster product development and more sustainable practices.
Processes that once required weeks could now be ready in hours.
Industry 5.0
The last revolution is human centric. Bringing the human back into the equation is one of the main pillars of Industry 5.0. It recognizes that technology should support, not replace, human intelligence.
By combining robotics, AI, and data science with human creativity, businesses can create personalized, sustainable, and meaningful products.
This means collaboration between humans and machines, like the return to craftsmanship enhanced by technology. Designers can use digital tools to craft unique garments tailored to each customer’s preferences.
Companies can growth while respecting the production limits of the planet, promoting responsible manufacturing.
Learn more: What is the fashion industry, its value, and key players?
Main challenges of Industry 5.0 in fashion
This new era promises incredible opportunities for the fashion sector, but it also comes with new challenges.
Brands must consider environmental, social, and operational impacts to succeed in this evolving industrial landscape.
Environmental impact and sustainability

Sustainability is at the heart of Industry 5.0, and fashion companies are under pressure to reduce their environmental footprint. Today, integrating eco-friendly practices is no longer optional: it’s a business necessity.
Advanced technologies can help mitigate environmental impact. For example, AI-driven production planning reduces overproduction, while digital prototyping and 3D printing cut fabric waste.
Smart materials, such as biodegradable or recyclable fabrics, also enable brands to create more sustainable collections.
Social responsibility and ethical issues
Industry 5.0 emphasizes human collaboration, which brings social responsibility to the forefront. Embracing ethical practices is essential for shaping the future of industry.
Fashion companies must ensure fair labor practices, equitable working conditions, and respect for employees throughout their supply chains. Ethical sourcing of materials and transparency in production are also crucial.
Balancing automation and human labor
One of the core promises of Industry 5.0 is intelligent automation, but machines should complement, not replace, human workers. Companies must find the right balance.
This approach ensures that humans remain at the centre of the production process, adding value where technology cannot.
Achieving this balance requires strategic workforce planning. The industry must invest in training and upskilling initiatives to prepare employees for collaborative roles alongside AI and robotics.
Learn more: Understand the importance of the textile industry and its evolution
Opportunities for fashion professionals in Industry 5.0
The doors the Industry 5.0 opens can translate to new jobs and growth. Professionals who embrace these changes can drive innovation, efficiency, and personalized experiences for consumers.
New roles and required skills
It creates a demand for new roles that blend creativity, technology, and strategic thinking.
Fashion professionals now need to understand digital tools, data analysis, and automation systems alongside traditional design skills. Knowledge of AI, 3D modeling, and smart textiles is becoming increasingly valuable.
Learn more: Key challenges in the garment industry and how to solve them
Improved efficiency and cost reduction
Industry 5.0 enables fashion companies to streamline production processes while reducing costs. Intelligent automation, data-driven planning, and predictive analytics allow brands to forecast demand accurately, minimize waste, and optimize resource use.
By integrating these technologies, companies can reduce overproduction and inventory costs.
Human workers can focus on tasks that require creativity and decision-making, while machines handle repetitive, time-consuming processes.
Ready to take your company to the next level and maximize productivity? Get our free exclusive guide filled with expert tips to make it happen!
Development of innovative and customized products
One of the most exciting opportunities of Industry 5.0 in fashion is the creation of highly innovative products. Technologies like 3D printing, augmented reality, and smart fabrics, allow brands to offer unique items.
In this scenario, customization goes beyond aesthetics: it includes functionality, comfort, and sustainability. For example, wearables or adaptive clothing can meet specific needs while maintaining a stylish design.
Learn more: Explore the benefits of industrial technology in the fashion sector
How to apply Industry 5.0 in the fashion sector
Applying Industry 5.0 concepts is about rethinking processes and combining technology with human creativity.
Here are some examples:
3D printing for garments and accessories
Designers can quickly create prototypes and test new ideas without the need for traditional production methods. This speeds up the development cycle and reduces material waste, making the process faster and more sustainable.
In addition to prototyping, 3D printing enables the creation of fully wearable garments and accessories. Brands can experiment with complex designs and shapes, that would be impossible or extremely costly with traditional manufacturing techniques.
This opens the door for innovation and creative freedom.
Augmented reality in the shopping experience
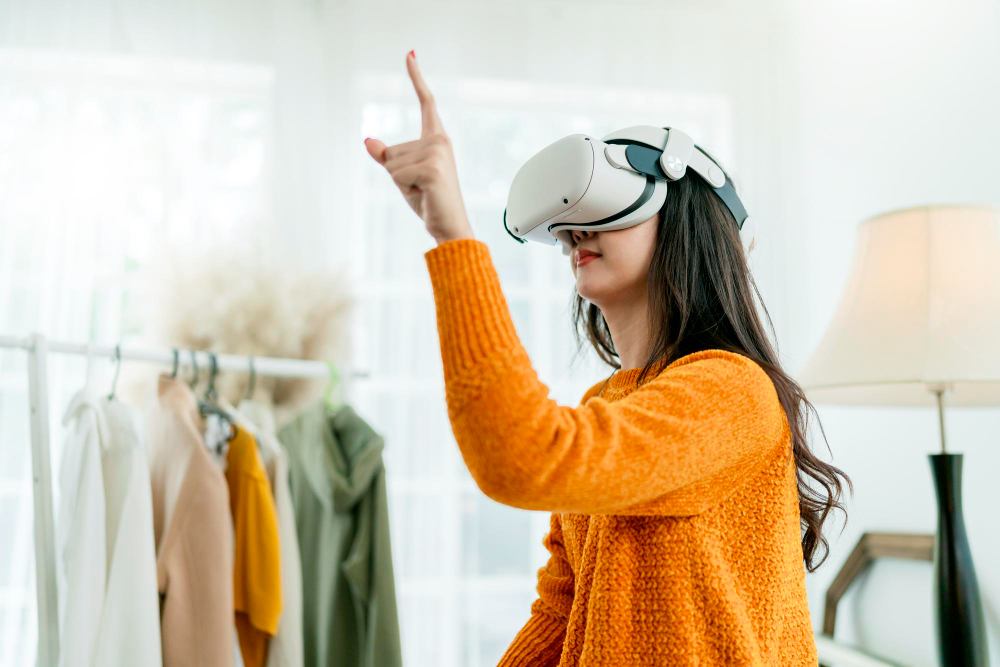

Augmented reality (AR) is changing how customers interact with fashion brands. Virtual try-on allows shoppers to see how garments, shoes, or accessories will look on them. All without visiting a physical store.
It also supports customization by letting customers experiment with colors, patterns, and styles in real time. Customers can personalize products digitally before placing an order, making the experience fun and highly tailored.
Learn more: Why is augmented reality in fashion a smart move?
Smart fabrics and wearables
These innovations combine textiles with sensors or electronics to offer new functions like temperature regulation and health monitoring. They allow fashion to move beyond aesthetics and into practical, interactive solutions.
The fusion of innovation and design encourages experimentation and sets brands apart in a competitive market.
From a business perspective, wearables and smart garments offer opportunities for personalized and value-added products. Customers receive items that are fashionable and functional, aligning perfectly with the human-centered focus of Industry 5.0.
Benefits of Industry 5.0 for clothing manufacturers
Companies that embrace this approach can stay competitive, reduce costs, and deliver products that better meet customer expectations.
Discover the key benefits:
Intelligent automation in apparel production
Intelligent automation allows fashion manufacturers to streamline repetitive and time-consuming tasks. This approach improves consistency and ensures high-quality output across all production lines.
By leveraging AI-powered systems, manufacturers can monitor operations in real time, predict maintenance needs, and reduce downtime. These actions lead to smoother workflows and better resource management.
Learn more: Enhance productivity in sectors of the textile industry with technology
Mass personalization

Advanced technologies allow manufacturers to produce clothing that fits individual customer preferences, from sizing and colors to patterns and fabric choices, without sacrificing efficiency.
For manufacturers, it helps balance small-batch production with cost-effectiveness.
Learn more: Top 5 technologies driving mass customization in clothing
On-demand manufacturing
On-demand manufacturing allows fashion companies to produce items only when needed, eliminating overproduction and reducing storage costs. This model is particularly valuable in an industry often challenged by fluctuating trends and seasonal demand.
With real-time data and AI forecasting, companies can respond quickly to customer orders, adjusting production schedules dynamically.
The flexibility improves cash flow, reduces waste, and enhances the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
Integration of advanced technologies
Industry 5.0 relies on the integration of advanced technologies to optimize production and enhance creativity. For example:
- IoT devices monitor machines and materials.
- AI predicts trends and automates repetitive tasks.
- Robotics handle precision work that improves speed and accuracy.
This technological synergy enables brands to maintain high-quality standards while exploring innovative processes.
Fashion companies can experiment with new designs, materials, and production methods that were previously impossible. Today, there are many incentives available to help businesses invest in these new technologies. It creates a competitive edge in a fast-moving market.
Learn more: Main incentives in industry to boost your business
Automate your business with audaces technologies
Follow the lead of Amibo, a Serbian brand known for its pajamas, underwear, and outdoor collections. The company started a digital transformation journey with Audaces to make its processes faster and more sustainable.
Discover how they did it!

Audaces360
Audaces360 integrates cutting-edge digital innovations to optimize workflows in the textile and apparel industry.
It caters to companies of all sizes and types, offering the flexibility to scale with your business needs.
All solutions were carefully developed to address the specific challenges of the field. They streamline the design and production processes, saving valuable time and resources.
The platform boasts a comprehensive range of functionalities, including pattern making, marking, collection management, vector drawing, and 3D creation.
In addition, a fashion Artificial Intelligence to assist you along the way.
Audaces Cutting Room
By embracing cutting-edge technology, garment manufacturers can achieve significant improvements in the production process. From greater design flexibility to enhanced efficiency and reduced costs.
This is where Audaces Cutting Room steps in. Our experts will thoroughly assess your company’s needs and create a comprehensive report.
Then, our team will develop a personalized project to achieve your goals and unlock your company’s full potential.
Rely on Audaces’ cutting-edge machinery to automate your production process. Achieve impeccable cuts on curves and details, speeding up your deliveries and minimizing fabric waste through automation.
Loved this article? Add our website to Google’s Top Store and stay connected with the latest in fashion tech!
FAQ
Industry 5.0 represents the next evolution in industrial development. One that brings the human element back into the center of innovation.
Environmental impact and sustainability, social responsibility and ethical issues, and balancing automation and human labor.
The possibilities include 3D printing, augmented reality in the shopping experience, and smart fabrics and wearables.











2 Responses
This post really sheds light on the transformative power of Industry 5.0 in fashion! I love how it emphasizes the blend of technology and sustainability. It’s exciting to see how personalized manufacturing and human creativity are reshaping the industry. Can’t wait to see more innovations in the future!
Thank you for your feedback! We’re glad you enjoyed the content and share the excitement about how Industry 5.0 is reshaping fashion through technology.
If you’d like to keep up with the latest insights, trends, and innovations in the industry, we invite you to subscribe to our newsletter and stay connected with our updates.