Summary:
- Textile automation makes repetitive tasks faster and safer, increasing the productivity of workers in the industry;
- The great advantage of automation for a textile company is that it allows more flexible and dynamic production lines. However, these are not its only benefits;
- Audaces is a superb ally for those who want their clothing manufacturing to stand out in Industry 4.0’s. Try Audaces360 multi-solution for free now!
Fashion and textile companies are always being tested by the market. Consumer behavior is changing all the time, as are global connections.
One of the main challenges these businesses will have to face in the coming years is the production process’s automation and the increasingly greater adoption of technology.
But do you know how your fashion company can benefit from textile automation?
Cost reduction is just one of the benefits entrepreneurs in the sector can take advantage of when using this technological resource.
Sumário
Find out more about this topic in the daily routines of many industries, which will become more and more common in the market.
Happy reading!
What is textile automation?
Textile automation is technology’s helping hand to boost productivity in the fashion industry with processes that used to be done manually. This way, anything that could only be done by hand now has machines and software to help with more speed and accuracy, avoiding errors.
For it to work properly, automation must be present throughout the production chain, ensuring optimization of time, greater competitiveness, and authority in the market.
Modern machines, software, and other technologies join forces with garment workers to produce much faster and more efficiently.
It’s also vital to remember that these improvements came up with Industry 4.0 and, for this reason, textile automation is part of industrial procedures.
Learn more: How does technology in fashion impact the textile industry?
Main benefits of automation in the textile industry

Automation in the industry offers major advantages. These processes are part of a larger framework of digital technologies revolutionizing all industrial sectors, including textiles.
According to Grand View Research, the global industrial automation and control systems market size was valued at 158.63 billion dollars in 2021 and is anticipated to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 10.3% from 2022 to 2030.
In addition, the institute says that, with the advent of Industry 4.0, the manufacturing sector has been experiencing quick adoption of new systems and augmented networking architectures.
When applied in industrial activity, these technologies benefit the operational efficiency and cost reduction, resulting in more flexible production lines and shorter product launch intervals.
For the Brazilian National Confederation of Industry (CNI), digitization is important for the industry in general because it enhances product improvement and encourages the creation of new business models.
An entity’s survey showed that, at the top of the ranking of automation, are the IT equipment, electronics, and optical products sectors, with 61% of their companies adopting digital technologies.
Industries that manufacture textile products appear in 6th place in the ranking of sectors that work with automated processes, with 35% of using. As a result, pieces are produced in less time with less labor force.
In summary, textile automation has numerous benefits for companies worldwide. It can result in improved customer satisfaction, as it reduces lead times and improves the accuracy of orders.
Inside the benefits of technological automation
The great advantage of textile automation in companies is that it brings flexible and dynamic daily processes.
- The main benefits of adopting automation-related technologies are the following:
- Establishment of flexible and autonomous production lines;
- Application of the mass customization concept;
- Reduction to a minimum efficient production scale;
- Better customer service with different tastes and needs;
- Reduction of operational and development costs;
- Increased productivity;
- Expansion of the market in which it operates;
- Improved product quality.
What are the most used automation technologies in the textile industry?

Another paper carried out by the CNI (Brazilian National Confederation of Industry) showed that from early 2016 to early 2018, the percentage of large companies that use at least one of the digital technologies considered in the surveys edged up from 63% to 73%. That is, 73% are already in Industry 4.0 in Brazil.
It also affirms that large industrial companies prioritize digital technologies to increase the efficiency of production processes and improve business management, particularly digital automation with process control sensors.
When it comes to the textile sector, automation became fundamental to gaining a sustainable competitive advantage through innovations in technology. Including computerized data monitoring, automatic fabric spreader, automatic fabric cutters, high-speed sewing machines, etc.
CAD software providing features like virtual test fitting and pattern and marker making, in addition to 3D designing, are strong examples already being put into practice in the textile industry.
Learn more: What is digital clothing and how does it impact the fashion industry?
How to apply automation technologies in the textile industry?
Textile automation is a practice that’s been growing every year, but it is worth emphasizing that technology and automated machines can contribute to the improvement of various sectors of the fashion industry.
Get to know 4 technologies for textile automation that can contribute to your company:
1. Team integration and data sharing
To share data, textile automation must be present throughout the production chain.
Machines and software can help you understand when maintenance is needed, in addition to updates on process steps, and other essential aspects.
On the other hand, the integrated equipment gives a good guide on how to improve other strategic sectors of the company, creating plannings and acting directly in places that need it.
2. Material control and inventory monitoring
Technology can bring greater control over your inputs. This is because textile automation helps in the management and control of your stock.
The systems can improve the analysis of information and data, and even the structure of sectors.
All that happens through the automation of activities such as receipt, storage, checking, movement, dispatch and issuing of documents.
3. Use of modeling and cutting software
Machinery using textile automation helps the company to reduce material wastage, production cost, and other key practices for sustainability. This is because it can identify failures and problems in real time.
In addition to improving the use of resources, textile automation impacts productivity, optimizing time and improving communication between sectors and teams.
4. Quality inspection
Some machines can boost the quality of many activities. With better cutting and pattern marking processes, the chances of having a flawless final product are way bigger!
Count on Audaces technologies for your company’s textile automation
Automation in the production processb by using modern equipment, such as the one from Audaces, helps clothing professionals to produce more and strive for the best quality!
Learn how to have all this with a company that is a world reference in technological innovation in fashion:
Cutting Room
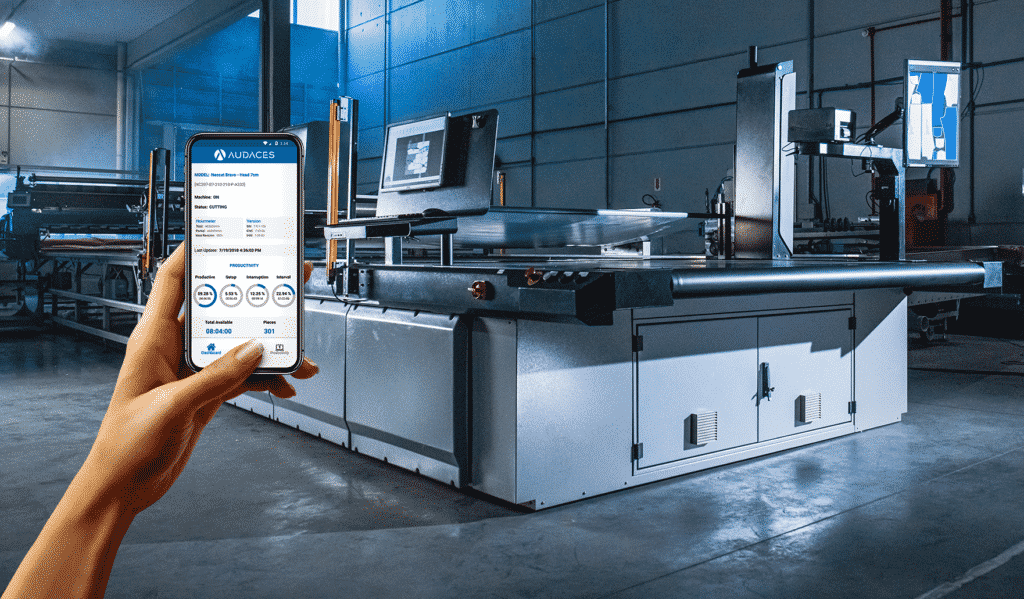
An automated cutting room allows excellent precision in cutting, in addition to optimizing the use of fabrics, minimizing leftovers and eliminating rework.
The pieces leave the cutting room ready for sewing, without needing further adjustments.
The cost reduction appears in the use of raw materials and the work hours spent by the team in the different stages of production.
All these gains mean that the company that invests in textile automation can obtain a much faster return on the investment made in equipment!
Audaces360
Audaces360 takes the integration and automation of the fashion supply chain to the next level!
From the creative phase to the development of specification sheets, from cost and feasibility forecasts to the creation of patterns, your collections will be visible and manageable in an easy, fast and optimized way.
Fashion designers, managers, assistants, technicians and pattern makers – all professions in the fashion industry find in Audaces360 the solution to overcome the most relevant market challenges.
Conclusion
Textile automation came to improve the fashion industry production. Machines and software bring more agility and uncountable gains to your company.
The future is already here – and technology is in charge! Download our free e-book now and learn more about the full potential of Industry 4.0:
FAQ
Textile automation is technology helping to boost productivity in the fashion industry with processes that used to be done manually.
More flexible and autonomous production lines, the reduction to a minimum efficient production scale, and better customer service, integration and quality inspection.
The larger textile companies prioritize digital technologies to increase the efficiency of production processes and improve business management.










